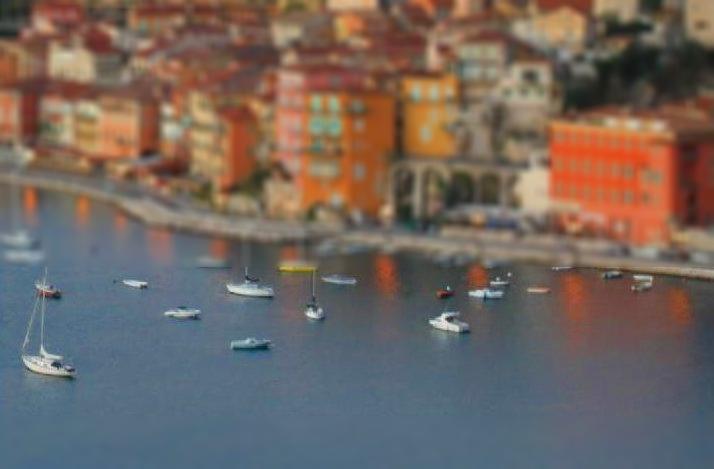Overview
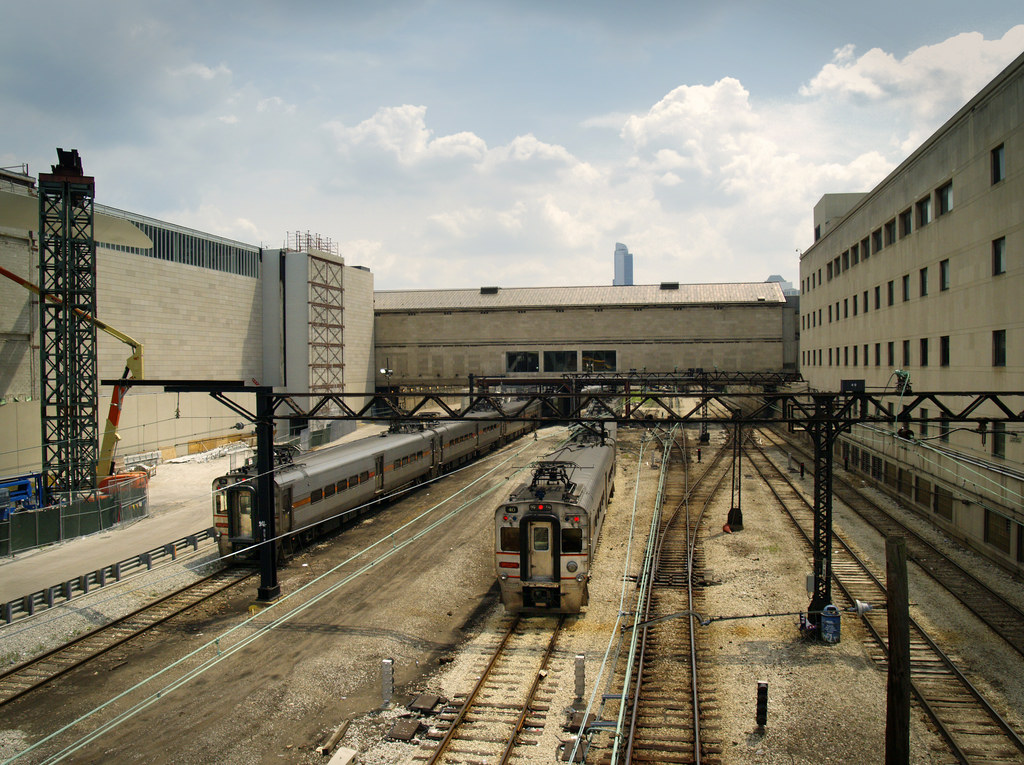
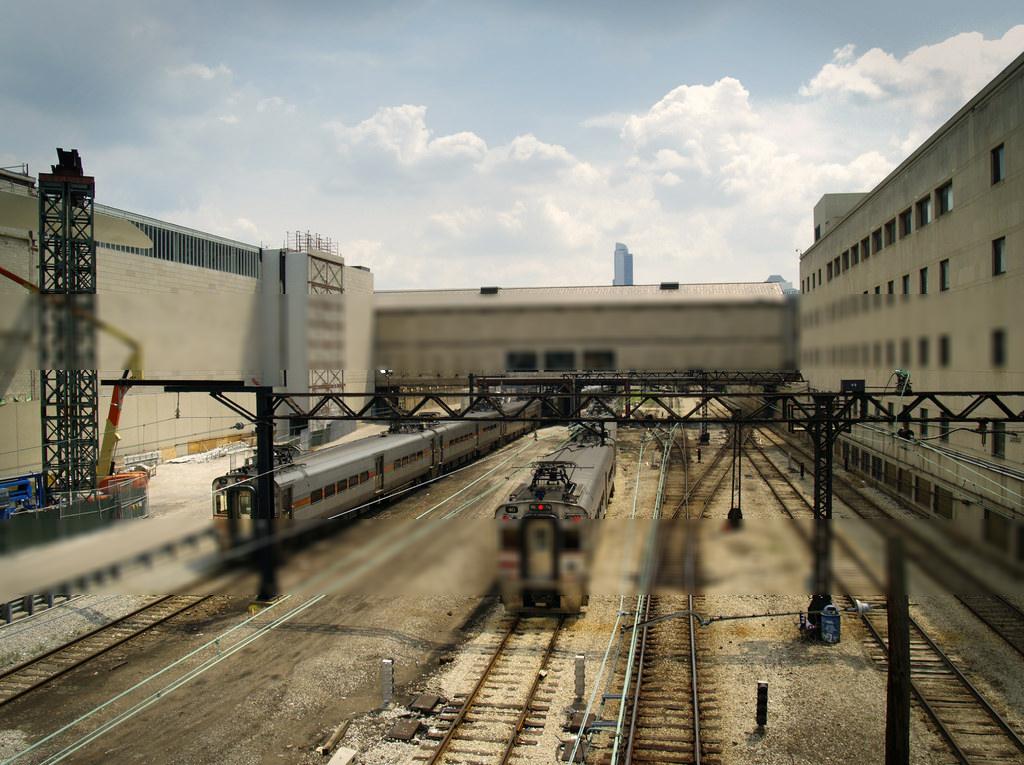
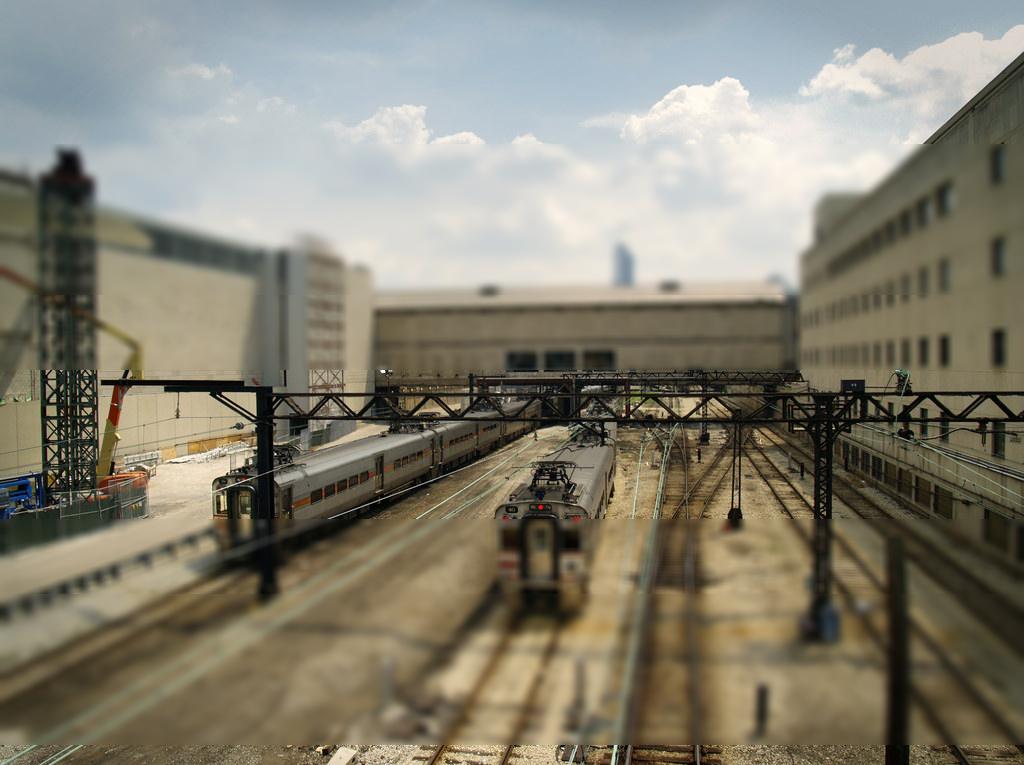
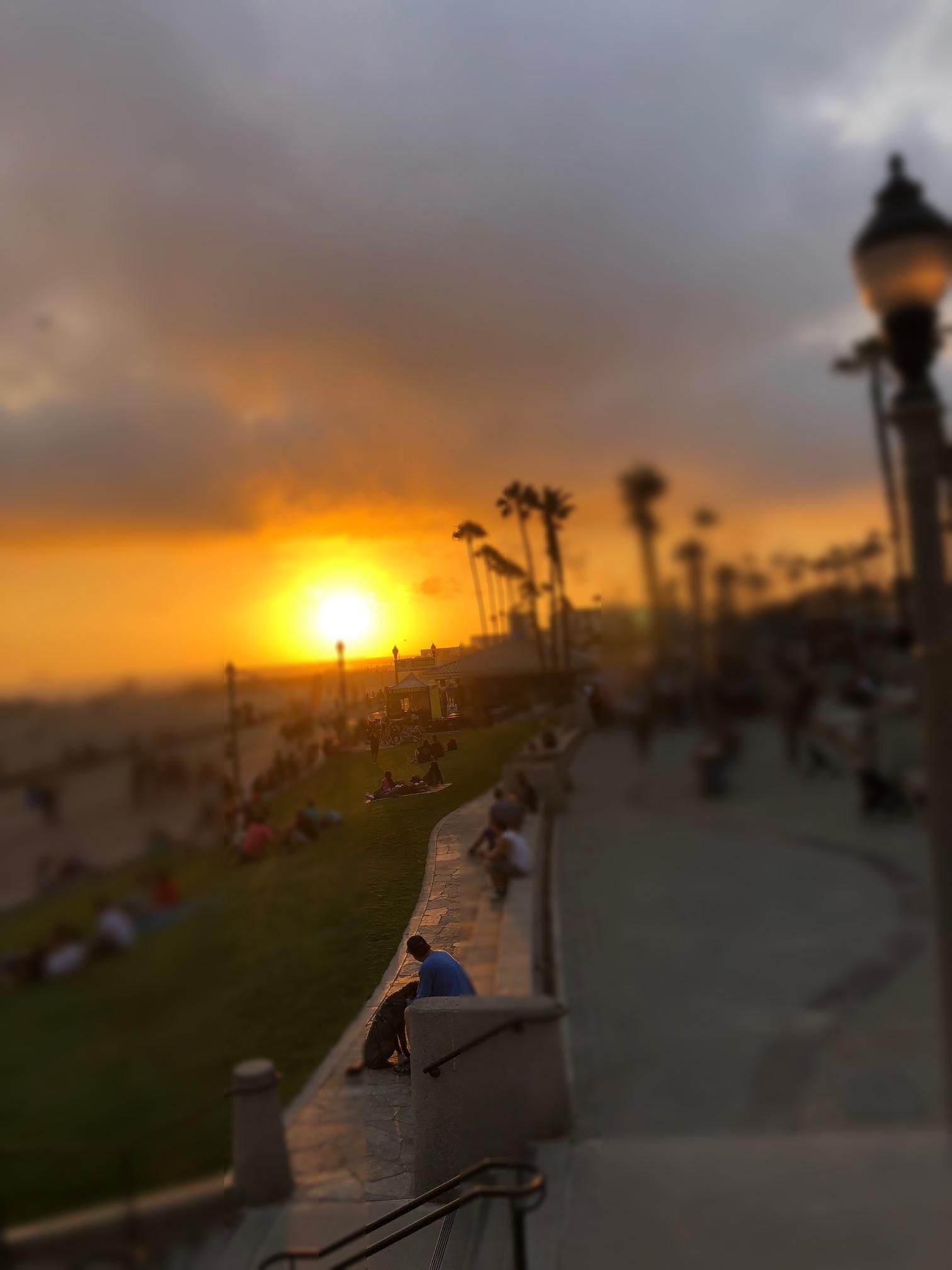
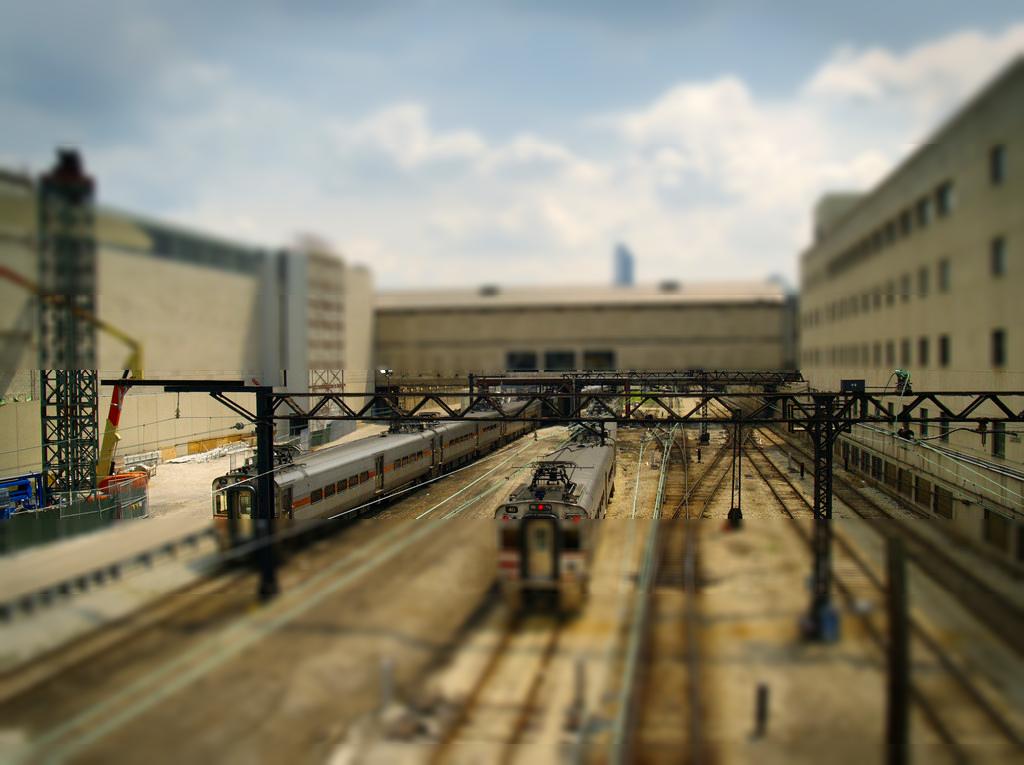
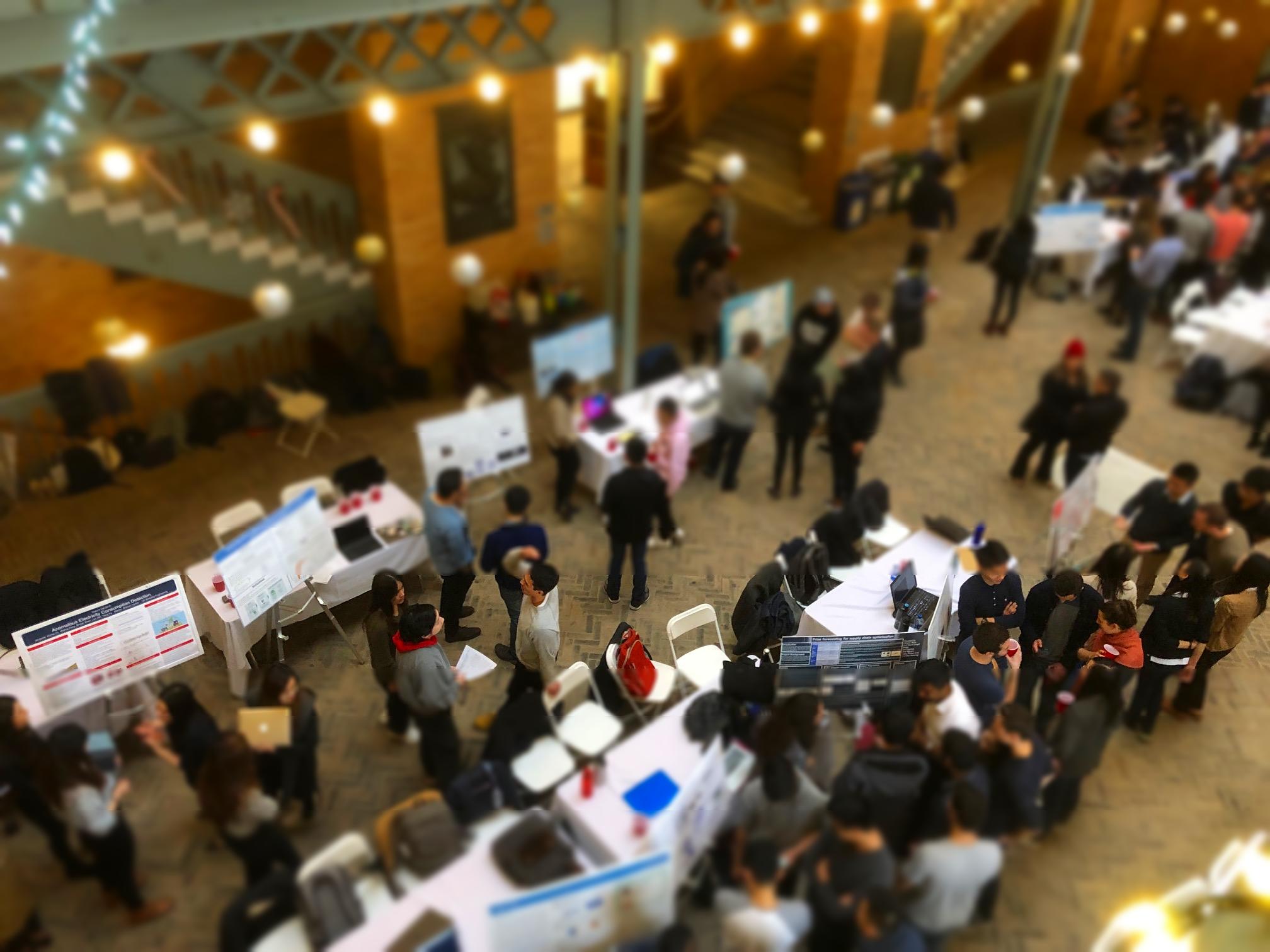
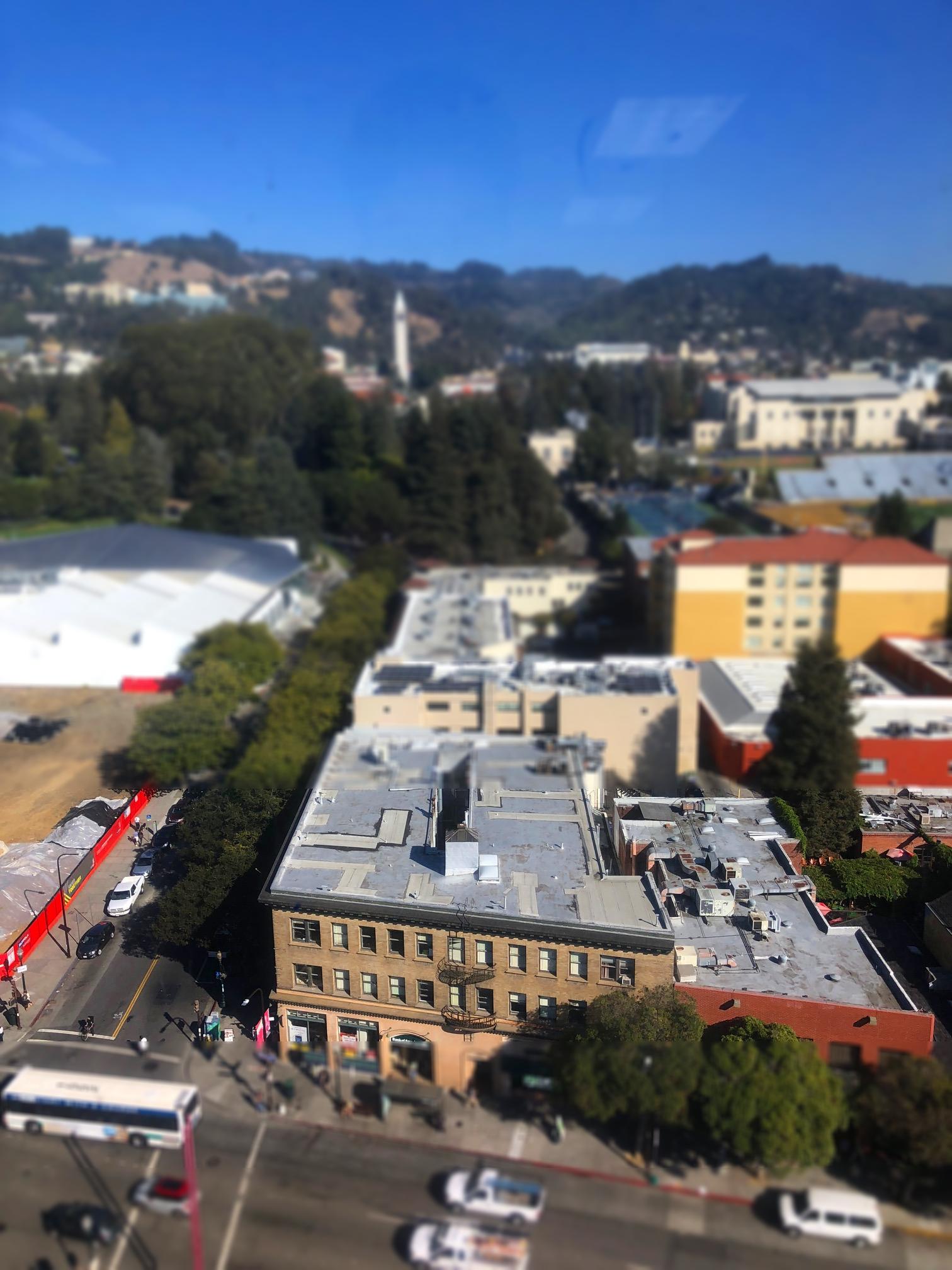
Miniatures are a cute imitation of real life. They're fake in a pleasant and palatable way. But what is it about miniature photography that exudes this spurious quality? This project identifies their oversaturated look, scale, and selective focus as the primary reasons. Tilt shift cameras are able to replicate the selective focus naturally with their ability to shift the depth of field in an atypical manner. But this effect can be achieved with selective blurring that will create the illusion that the camera was actually really close to the subject.
Part 1: Setting the Focus Line
A focus line will determine the area in our fake miniature on which the camera is focusing on. A good focus line will highlight objects which would realistically be included in the same depth of field if they were miniatures.
The focus line is set by selecting two points off the original image. The first point will mark the center of the dof. The second point determines how large the dof area will be. By selecting the points on a "per image" basis, different size images can be used without worry.
Summary
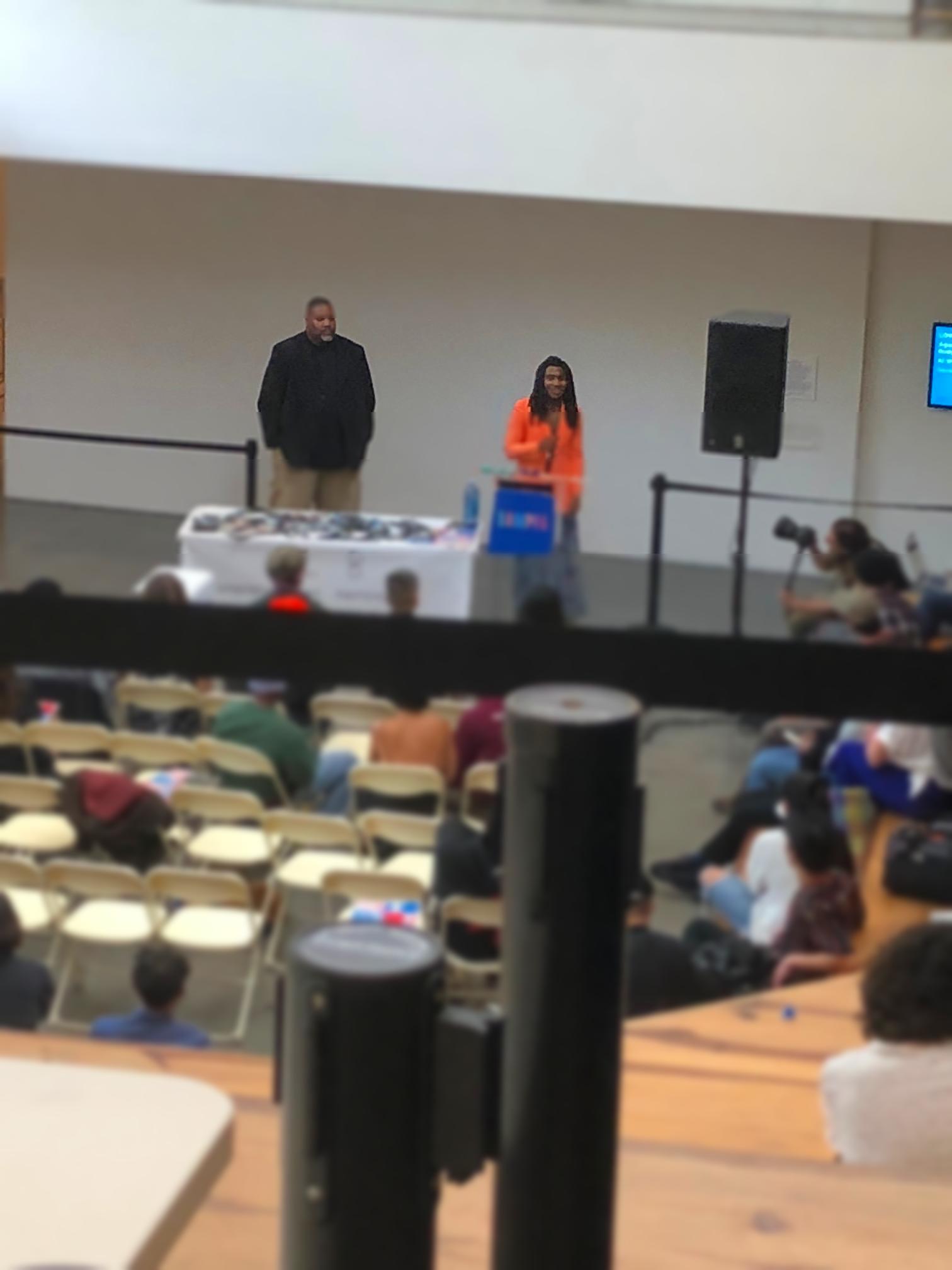
Achieving a miniature-like image doesn't exactly rely on the most complex of techniques we've learned in this class. Like Professor Efros says, the most important component of image manipulation is the image itself. As seen in the failed miniature of Lil B, the proper perspective and objects to group in the depth of field are essential to fooling the viewer.