
| CS 39J > Schedule & Notes > Session 10 Detailed Notes |
http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs39j/session10.html
4 April 2002
You can do many things with Photoshop:

Hockey photograph at the Winter Olympics 2002, from Wacom Incorporated


Closing The Gap Between ASIC & Custom cover design
by Steven Chan, 2002.
Clinton photo from "Clinton
Declares Self President for Life" by The Onion, 2001.

X-Men Evolution comic book cover ©Marvel Comics. Art by Udon Comics.
Kawaldeep Grewal
Viet Nguyen & Steve
Download his handout on color casts here!
catalogshot kawaldeep wheeler face
|
Start Photoshop as usual. If you don't know how, read last session's handouts or ask a "T.A.". Then, download the picture on the right using this link (TIFF) or this link (JPEG). This picture needs a serious facelift. It's the picture of this Chinese guy who stands on his bucket and stool all day long in front of Telegraph. In case his pro-China propaganda offends people, I've secretly replaced his signs with more peaceful words. What's wrong with this picture? (besides the sign) What kinds of things can be done to improve this picture? Goal: to make a picture focussing on the guy. And maybe give it some rustic appeal. |
 |

Photoshop gives us a variety of ways to adjust the colors. We'll try two of the methods today.
|
Brightness/Contrast
|
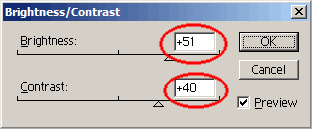 |
|
Levels
|
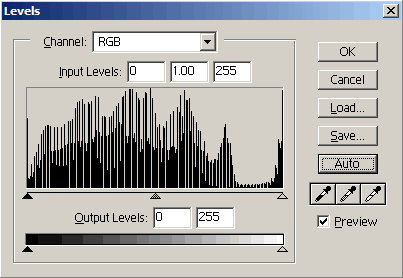 |
 |
Try adjusting this discolored photo of Sproul Plaza for more practice. |

Cropping is relatively straightforward. Photoshop's crop tool allows you to select the area that you want to keep. It also allows you to rotate an area.
|
You usually want to crop out parts of a photograph that are irrelevant and unnecessary. For example, what could we crop out in this photograph? |
 |
|
Crop
|
 |
trace the man's outline.
Adapted from The Photoshop 6 Wow! Book (Dayton & Davis), page 120, and Maine.com.

Sepia helps give a photograph an antique, rustic mood, primarily used in old black and white photographs. Ironically, this photo of the Berkeley BART station here is by no means antique, but if you compare the Original and the Sepia photos above, the Sepia effect better conveys a feeling, perhaps of isolation or longing. In traditional photographs, sepia tones exist because its black & white paper has deteriorated.
|
Basically, we apply a brown color to the image. The easiest way:
|
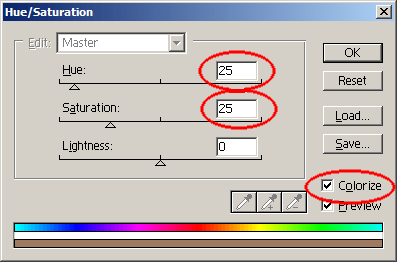 |

The crop tool is actually a particular instance of a family of tools named "Selections." Selections allow you to pick and choose a particular portion of an image, and fiddle with it to your heart's content. Whatever colors you adjust, for example, only affects your selected area.
In our example picture, we're going to experiment a little bit with the man's head.
|
Rectangular Marquee and Move
|
 |
This next bit will be a little more complicated. We're going to trace the man's full outline.
|
Lasso
|
 |
You can do lots of fancy things with filters. They are an essential part of a graphic designer's work, but they are also an important tool for professional photography editing. Let's take the Doe Library for example.
We can distort the library to make it look (kinda) like a swimming pool's reflection ...

... we can blur the colors together ...

...and we can add stuff to the image.

Explore through the Filters menu and write down the effects you particularly like. Experiment on our example man, or you can use the photograph of the Doe Library here.
For the next part, we will use a filter to blur the background.
Adapted from The Photoshop 6 Wow! Book (Dayton & Davis), page 140-43.

We can blur the background to imitate a shortened depth-of-field. It's especially useful in these areas:
|
The Cheap, Easy Way
|
|
The Harder, Better-Looking Way
|
|
|
|
Preparing the next few layers
|
|
|
|
Blurring the background
|
|
|
|
Your photograph should look like the first one on the right. I encourage you to be creative. You can do lots of cool things with Photoshop, like a psychedelic acid trip to the 70's. Groovy. |
 |
Softening Focus
wow! page 130-1
- need photo of "still life."
Dust & Scratches
wow! page 134-6
Painting
Dodge & Burn
Retouching
Note: All photos on this page are ©2001-2002 Steven Chan. Duplication prohibited. All rights reserved. So don't stealie, or you just might wake up screaming . . . mwahaha.
  |
|