Homework 8: Scheme
Due by 11:59pm on Thursday, November 17
Instructions
Download hw08.zip. Inside the archive, you will find a file called
hw08.scm, along with a copy of the ok autograder.
Submission: When you are done, submit with python3 ok
--submit. You may submit more than once before the deadline; only the
final submission will be scored. Check that you have successfully submitted
your code on okpy.org. See Lab 0 for more instructions on
submitting assignments.
Using Ok: If you have any questions about using Ok, please refer to this guide.
Readings: You might find the following references useful:
Grading: Homework is graded based on correctness. Each incorrect problem will decrease the total score by one point. There is a homework recovery policy as stated in the syllabus. This homework is out of 2 points.
Scheme is a famous functional programming language from the 1970s. It is a dialect of Lisp (which stands for LISt Processing). The first observation most people make is the unique syntax, which uses a prefix notation and (often many) nested parentheses (see http://xkcd.com/297/). Scheme features first-class functions and optimized tail-recursion, which were relatively new features at the time.
Recommended VSCode Extensions
If you use VSCode as your text editor, we have found these extensions to be quite helpful for Scheme :)
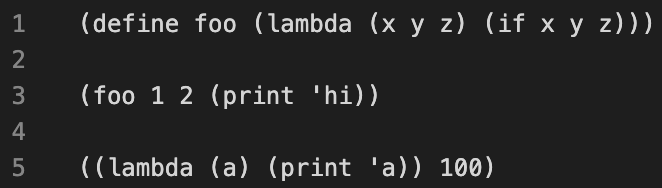
Before:
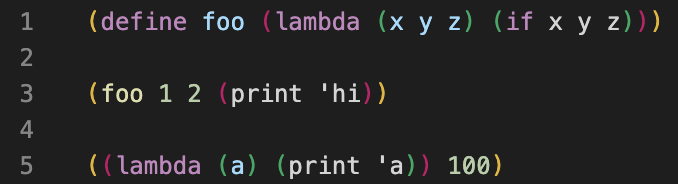
After:
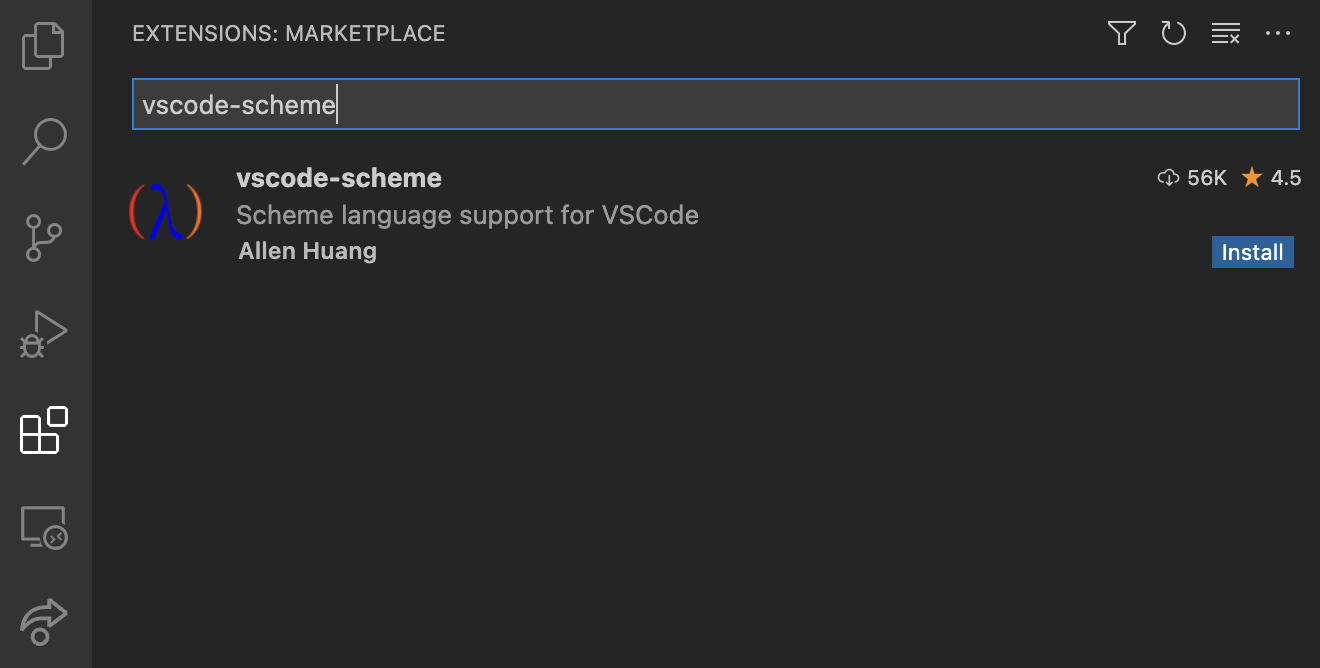
Extensions:
You may find it useful to try code.cs61a.org/scheme when working through problems, as it can draw environment and box-and-pointer diagrams and it lets you walk your code step-by-step (similar to Python Tutor). Don't forget to submit your code through Ok though!
Scheme Editor
You can write your code by either opening the designated .scm file in your text editor, or by typing directly in the Scheme Editor, which can also be useful for debugging. To run this editor, run python3 editor. This should pop up a window in your browser; if it does not, please navigate to localhost:31415 while python3 editor is still running and you should see it. If you choose to code directly in the Scheme Editor, don't forget to save your work before running Ok tests and before closing the editor. To stop running the editor and return to the command line, type Ctrl-C.
Make sure to run python3 ok in a separate tab or window so that the editor keeps running.
If you find that your code works in the online editor but not in your own interpreter, it's possible you have a bug in your code from an earlier part that you'll have to track down. Every once in a while there's a bug that our tests don't catch, and if you find one you should let us know!
Required Questions
Getting Started Videos
These videos may provide some helpful direction for tackling the coding problems on this assignment.
To see these videos, you should be logged into your berkeley.edu email.
Q1: My Filter
Write a procedure my-filter, which takes a predicate pred and a list s, and
returns a new list containing only elements of the list that satisfy the
predicate. The output should contain the elements in the same order that they
appeared in the original list.
Note: Make sure that you are not just calling the built-in filter function in Scheme - we are asking you to re-implement this!
(define (my-filter pred s)
'YOUR-CODE-HERE
)Use Ok to unlock and test your code:
python3 ok -q filter -u
python3 ok -q filterQ2: Interleave
Implement the function interleave, which takes a two lists lst1 and lst2 as
arguments. interleave should return a new list that interleaves the elements
of the two lists. (In other words, the resulting list should contain elements
alternating between lst1 and lst2.)
If one of the input lists to interleave is shorter than the other, then
interleave should alternate elements from both lists until one list has no
more elements, and then the remaining elements from the longer list should be
added to the end of the new list.
(define (interleave lst1 lst2)
'YOUR-CODE-HERE
)Use Ok to unlock and test your code:
python3 ok -q interleave -u
python3 ok -q interleaveQ3: Accumulate
Fill in the definition for the procedure accumulate, which joins the first
n natural numbers (ie. 1 to n, inclusive) according to the following parameters:
joiner: a function of two argumentsstart: a number with which we start joiningn: the number of natural numbers to jointerm: a function of one argument that computes the nth term of a sequence
For example, we can find the product of all the numbers from 1 to 5 by
using the multiplication operator as the joiner, and starting our
product at 1:
scm> (define (identity x) x)
scm> (accumulate * 1 5 identity) ; 1 * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5
120We can also find the sum of the squares of the same numbers by using the
addition operator as the joiner and square as the term:
scm> (define (square x) (* x x))
scm> (accumulate + 0 5 square) ; 0 + 1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2
55
scm> (accumulate + 5 5 square) ; 5 + 1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2
60You may assume that the joiner will always be commutative: i.e. the order
of arguments do not matter.
(define (accumulate joiner start n term)
'YOUR-CODE-HERE
)Use Ok to unlock and test your code:
python3 ok -q accumulate -u
python3 ok -q accumulateQ4: No Repeats
Implement no-repeats, which takes a list of numbers lst as input and returns
a list that has all of the unique elements of lst in the order that they first
appear, but no repeats. For example, (no-repeats (list 5 4 5 4 2 2))
evaluates to (5 4 2).
Hint: How can you make the first time you see an element in the input list be the first and only time you see the element in the resulting list you return?
Hint: You may find it helpful to use the
my-filterprocedure with a helperlambdafunction to use as a filter. To test if two numbers are equal, use the=procedure. To test if two numbers are not equal, use thenotprocedure in combination with=.
(define (no-repeats lst)
'YOUR-CODE-HERE
)Use Ok to unlock and test your code:
python3 ok -q no_repeats -u
python3 ok -q no_repeats