Projection on a polyhedron
Recall that a polyhedron is an intersection of a finite number of half-spaces. A polyhedron 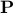 can be written as
can be written as
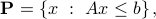
where 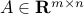 and
and 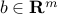 , and the symbol
, and the symbol  refers to the component-wise inequality between vectors.
refers to the component-wise inequality between vectors.
The Euclidean projection (or projection for short) of the origin on the polyhedron 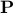 is the (unique) solution to the optimization problem
is the (unique) solution to the optimization problem

Without loss of generality, we can square the objective and solve the problem

The above is a QP.