Dimension of an affine subspace
The set 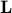 in
in  defined by the linear equations
defined by the linear equations

is an affine subspace of dimension  . The corresponding linear subspace is defined by the linear equations obtained from the above by setting the constant terms to zero:
. The corresponding linear subspace is defined by the linear equations obtained from the above by setting the constant terms to zero:

We can solve for 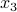 and get
and get 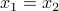 ,
,  . We obtain a representation of the linear subspace as the set of vectors
. We obtain a representation of the linear subspace as the set of vectors  that have the form
that have the form

for some scalar  . Hence the linear subspace is the span of the vector
. Hence the linear subspace is the span of the vector  , and is of dimension
, and is of dimension  .
.
We obtain a representation of the original affine set by finding a particular solution 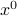 , by setting say
, by setting say  and solving for
and solving for  . We obtain
. We obtain

The affine subspace 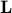 is thus the line
is thus the line  , where
, where  are defined above.
are defined above.