Permutation matrices
A 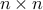 matrix
matrix 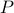 is a permutation matrix if it is obtained by permuting the rows or columns of an
is a permutation matrix if it is obtained by permuting the rows or columns of an 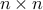 identity matrix according to some permutation of the numbers
identity matrix according to some permutation of the numbers  to
to 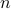 . Permutation matrices are orthogonal (hence, their inverse is their transpose:
. Permutation matrices are orthogonal (hence, their inverse is their transpose: 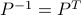 ) and satisfy
) and satisfy 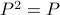 .
.
For example, the matrix
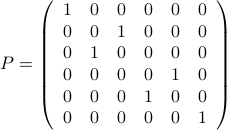
is obtained by exchanging the columns 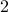 and
and 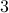 , and
, and 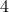 and
and 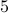 , of the
, of the 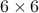 identity matrix.
identity matrix.
A permutation matrix allows to exchange rows or columns of another via the matrix-matrix product. For example, if we take any 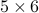 matrix
matrix 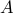 , then
, then 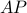 (with
(with 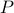 defined above) is the matrix
defined above) is the matrix 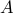 with columns
with columns 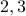 and
and 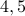 exchanged.
exchanged.