Linearization of a non-linear function
The log-sum-exp function

admits the gradient at the point 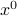 given by
given by

Hence 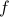 can be approximated near
can be approximated near 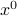 by the linear function
by the linear function

Linearization of a non-linear functionThe log-sum-exp function 
admits the gradient at the point 
Hence 
|