Representation of a two-variable quadratic function
Symmetric Matrices > Definitions > Example
The quadratic function  , with values
, with values

can be represented via a symmetric matrix, as

In short:

where 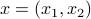 , and
, and

Representation of a two-variable quadratic functionSymmetric Matrices > Definitions > Example
The quadratic function 
can be represented via a symmetric matrix, as 
In short: 
where 
|