Half-Spaces
Definition
Geometry
Link with linear functions
Definition
A half-space is a set defined by a single affine inequality. Precisely, a half-space in 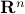 is a set of the form
is a set of the form
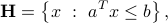
where 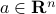 ,
, 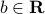 . A half-space is a convex set, the boundary of which is a hyperplane.
. A half-space is a convex set, the boundary of which is a hyperplane.
A half-space separates the whole space in two halves. The complement of the half-space is the open half-space 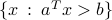 .
.
 |
When 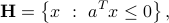
is the set of points which form an obtuse angle (between |
Example: A half-space in 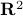 .
.
Link with linear functions
Hyperplanes correspond to level sets of linear functions.
Half-spaces represent sub-level sets of linear functions: the half-space above describes the set of points such that the linear function 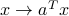 achieves the value
achieves the value 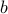 , or less. A quick way to check which half of the space the half-space describe, is to look at where the origin is: if
, or less. A quick way to check which half of the space the half-space describe, is to look at where the origin is: if 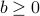 , then
, then 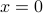 is in the half-space.
is in the half-space.
 , the half-space
, the half-space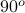 and
and  ) with the vector
) with the vector  . The boundary of this set is a subspace, the hyperplane of vectors orthogonal to
. The boundary of this set is a subspace, the hyperplane of vectors orthogonal to 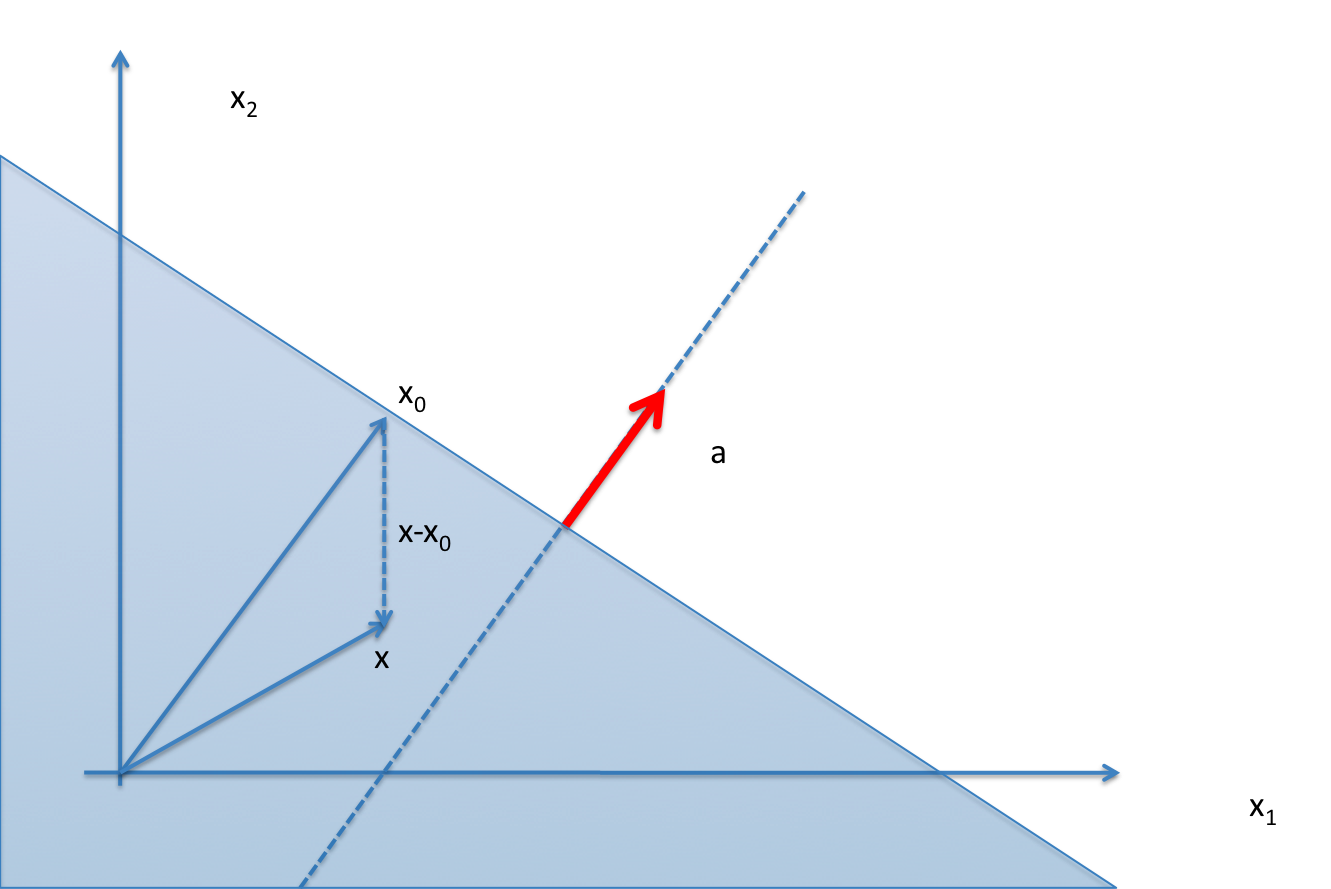
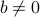 , the corresponding half-space can be written as
, the corresponding half-space can be written as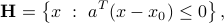
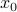 is chosen such that
is chosen such that 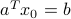 . For example,
. For example, 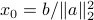 is such a point on the boundary of the half-space (this particular choice corresponds to the minimum-norm solution to the equation
is such a point on the boundary of the half-space (this particular choice corresponds to the minimum-norm solution to the equation 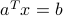 ). Thus, the half-space above corresponds to the set of points such that
). Thus, the half-space above corresponds to the set of points such that 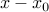 (shown in dotted) forms an obtuse angle with the vector
(shown in dotted) forms an obtuse angle with the vector