|
|
|
|
|
CS180/280A: Intro to Computer Vision and Computational
Photography
|
INSTRUCTOR:
Alexei (Alyosha) Efros
(Office hours: after lecture),
Angjoo Kanazawa
(Office hours: after lecture)
GSI:
Ruilong Li
(DIS: Tue. 1PM - 2PM, OH: Tue. 3PM - 4PM), Jake
Austin (DIS: Tue 11AM - 12PM, OH: Thu. 2PM - 3PM)
Tutors:
Max Vogel
(OH: Mon. 10AM - 11AM), Morgan Lyu
(OH: Tue. 4PM - 5PM), Preston McCrary (OH: Fri. 2PM - 3PM)
UNIVERSITY UNITS: 4
SEMESTER: Fall 2023
WEB PAGE:
https://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs180/fa23/
Google Calender:
c_5e316e16608c028a04d3ab19f4cff1e73a6796ef0d559c549f9e1f8f14f30751@group.calendar.google.com
(Public URL)
Ed:
https://edstem.org/us/courses/42166/
Gradescope Entry Code:
57Y3YJ
Syllabus:
here
LOCATION: Li Ka Shing 245
TIME : MW 5:00 PM-6:30 PM
PREREQUISITES:
This is a heavily project-oriented class, therefore good programming
proficiency (at least CS61B) is absolutely essential. Moreover,
familiarity with linear algebra (MATH 54 or EE16A/B or
Gilbert Strang's online
class) and calculus are vital. Experience with neural networks (e.g.
CS182 or equivalent) is strongly recommended. Due to the
open-endedness of this course, creativity is a class
requirement.
COURSE DESCRIPTION:
The aim of this advanced undergraduate course is to introduce students
to computing with visual data (images and video). We will cover
acquisition, representation, and manipulation of visual information
from digital photographs (image processing), image analysis and visual
understanding (computer vision), and image synthesis (computational
photography). Key algorithms will be presented, ranging from classical
(e.g. Gaussian and Laplacian Pyramids) to contemporary (e.g. ConvNets,
GANs), with an emphasis on using these techniques to build practical
systems. This hands-on emphasis will be reflected in the programming
assignments, in which students will have the opportunity to acquire
their own images and develop, largely from scratch, the image analysis
and synthesis tools for solving applications.
PROGRAMMING ASSIGNMENTS: TO BE ANNOUNCED.
|
Project 1: Images of the Russian Empire -- Colorizing the
Prokudin-Gorskii Photo
Collection
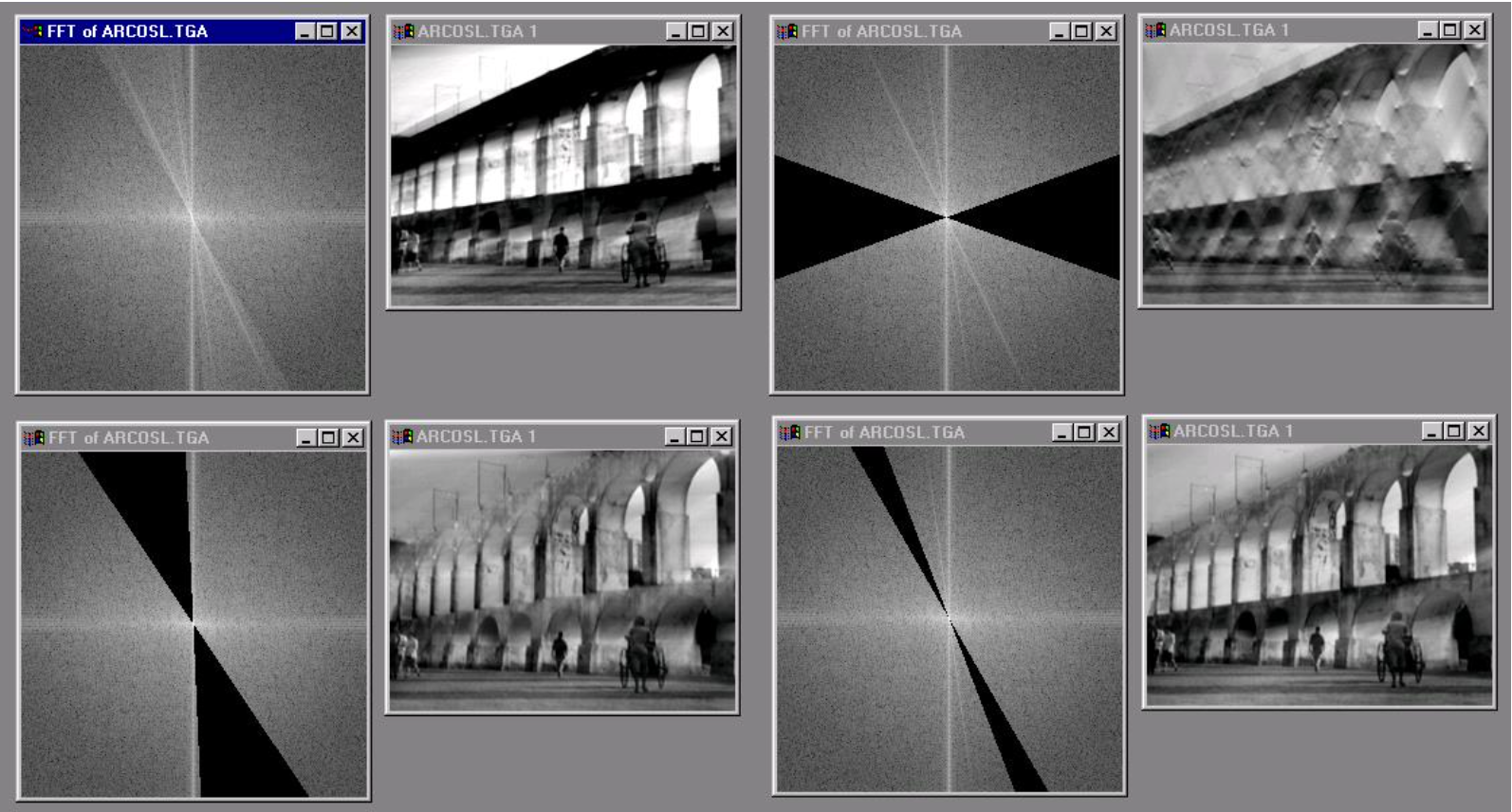
Project 2: Fun with Filters and Frequencies
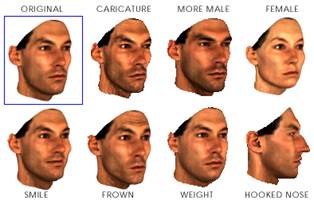
Project 3: Face Morphing and Modelling a Photo Collection
Project 4: (Auto)stitching and photo mosaics
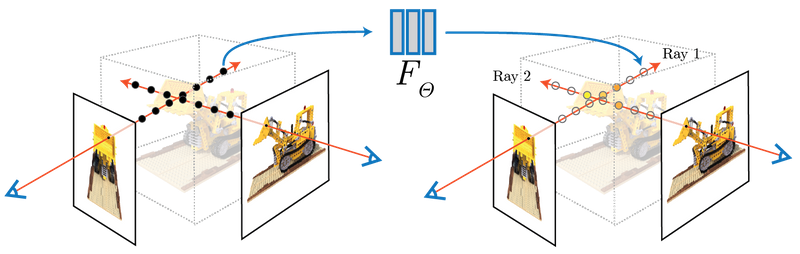
Project 5: Neural Radiance Fields
|
TEXTBOOK:
We will be loosely using the new 2nd edition of
Rick Szeliski's Computer Vision textbook. You can purchase a hard copy or use a
free pdf.
There is a number of other fine texts that
you can use for general reference:
Computer Vision: A Modern Approach (2nd edition), Forsyth
and Ponce (classic computer vision text)
Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology, Stephen Palmer
(great book on human visual perception)
Digital Image Processing, 2nd edition, Gonzalez and Woods
(a good general image processing text)
Linear Algebra and its Applications, Gilbert
Strang
(a truly wonderful book on linear algebra)
CLASS NOTES
The instructor is extremely grateful to a large number of researchers
for making their slides available for use in this course.
Steve Seitz
and
Rick Szeliski
have been particularly kind in letting me use their wonderful lecture
notes. In addition, I would like to thank
Paul Debevec, Stephen Palmer,
Paul Heckbert, David Forsyth,
Steve Marschner
and others, as noted in the slides. The instructor gladly gives
permission to use and modify any of the slides for academic and
research purposes. However, please do also acknowledge the original
sources where appropriate.
CLASS SCHEDULE:
|
CLASS DATE |
TOPICS |
Material |
|
Aug |
Introduction |
|
|
Aug |
Capturing Light... in man and machine |
|
|
Aug |
Image Processing I |
|
|
Sep |
Image Processing II: Convolution and Derivatives |
|
|
Sep |
The Frequency Domain |
|
|
Sep |
Pyramid Blending, Templates, NL Filters |
|
|
Sep |
Image Transformations |
|
|
Sep |
Image Warping and Morphing |
|
|
Sep |
Data-driven Methods: Faces |
|
|
Sep |
The Camera |
|
|
Oct |
Homographies and Mosaics |
|
|
Oct |
More Mosaics |
|
|
Oct |
Automatic Image Alignment |
|
|
Oct |
3D Vision: Intro |
|
|
Oct |
Stereo |
|
|
Oct |
Epipolar |
|
|
Oct |
SfM and MVS |
|
|
Oct |
MVS & Neural Radiance Fields |
|
|
Oct |
Neural Radiance Fields 2 |
|
|
Nov |
Neural Radiance Fields 3 |
|
|
Nov |
Visual Texture |
|
|
Nov |
Sequence Models for Words and Pixels. |
|
|
Nov |
Generative Models. |
|
|
Nov |
HDR + IBL |
|
|
Nov |
Morden Art |
|
CAMERAS:
Although it is not required, students are highly encouraged to
obtain a digital camera for use in the course.
METHOD OF EVALUATION:
Grading will be based on a set of programming and written
assignments (60%), a final exam + potentially some Pop Quizzes
(20%), and a final project (20%). For the
programming assignments, students will be allowed a total of 5
(five) late days per semester; each additional late day will incur a
10% penalty.
Students taking CS280A will also be required to submit a
conference-style paper describing their final project.
PROGRAMMING RESOURCES:
:
Students will be encouraged to use either Python (with either
scikit-image or opencv) or MATLAB (with the Image Processing
Toolkit) as their primary computing platform.
Specific libraries in both languages offer tons of built-in image
processing functions.
Here is a link to some
useful MATLAB and Python resources
compiled for this class.
PREVIOUS OFFERINGS OF THIS COURSE:
:
Previous offerings of this course can be found
here.
SIMILAR COURSES IN OTHER UNIVERSITIES:
-
Computational Photography
(Hoiem, UIUC)
-
Computational Photography
(Hays, Brown)
-
Digital and Computational Photography
(Durand, MIT)
-
Computer Vision
(Seitz & Szeliski, UWashington)
Page design courtesy of
Doug James
![Description: [SCS dragon logo]](463_files/ucbseal_139_540.png)

 Class Choice Awards:
Class Choice Awards:  Runner ups:
Runner ups: